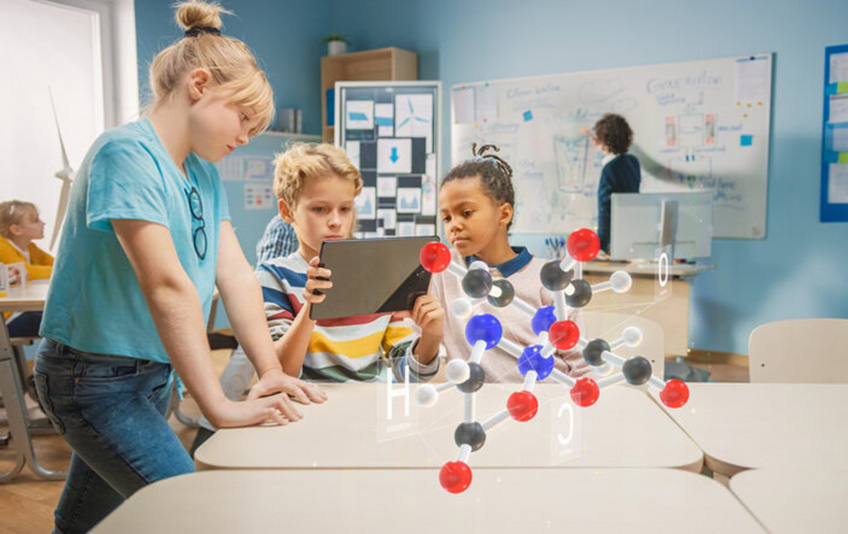
Augmented Reality (AR) has become an advanced and advantageous technology in many fields. Among all kinds of benefits, AR has a magnificent potential to be a great educational and analytical tool for learning or interpreting of the complicated structures in some scientific fields such as chemistry for students and teachers as well as scientists.
In this article, we will discuss several difficulties of learning chemistry in 2D, some noteworthy benefits of using AR in chemistry, and furthermore introducing a number of applications for applying AR in chemistry learning.
Difficulties of learning chemistry in 2D
In some fields of sciences, for instance, chemistry, the challenge of visualizing the 3D complex structures into 2D dimension space, such as on paper or a screen exists at several levels. Visualizing could be peculiarly challenging while the combinations are growing into more complex and larger compounds.
In 2D images, atoms and chemical bonds are overlapping, thus the symmetry and geometry of the structures are difficult to visualize.
Schematic or simplified drawings of molecules have been the only way to illustrate and describe the geometry and symmetry of complicated structures which could easily lead to neglecting the vital information.
The benefits of using AR in learning chemistry
Applying AR as a professional approach can transform visualization in chemistry learning. It provides a great opportunity to understand the structures from all angles, visualize how atoms and bonds are arranged as well as apprehend more abstract chemical concepts such as carbon hybridization
By providing a 3D perspective, AR would help more ubiquitous and collaborative learning in classrooms and even in lectures. It can supply students a sense of immediacy, presence, and immersion, and even the ability to manipulate the structures virtually. All learners by using AR would be provided with opportunities in contextualization and authenticity while conveying the chemical structures.
While the learning process is provided by Augmented Reality, the chance for more integration into context and also the discourse between teacher and students as well as students and students increase.
Many of the AR applications are effortlessly performed on smartphones. Using AR in mobile phones will change students’ perceptions from their own devices and shift from a mere communication device into a learning instrument.
Some examples of augmented reality in chemical structures
In spite of being a breakthrough element, AR has not been widely applied in chemical studies. Thanks to several recent studies and successfully being tested in some schools, there are several applications developed to be used on smartphones and tablets for learning chemical structure more efficiently. Several examples of these applications are listed below:
1) “Merge” app: it is a free AR application that is combined with a “Merge cube” to allow users to physically hold and be more practically engaged in 3D objects. The movement of the cube is transferred into a movement of the projected model.
2) AR chemistry learning was built specifically for educational purposes.
3) Learn with the manual: this application is based on text recognition. By using this app, the required information will be displayed by certain words that represent the name of substances.
4) Learn with the cards: some cards are prepared in Adobe Illustrator. These cards contain the full name of the substance, the chemical formula, and the periodic table of Mendeleev. The cards could be recognized in the Vuforia component and also in a database called “ArLearn”.
5) The Organic Molecule AR/VR cards: these cards have two features of learning and playing games by using the corresponding application.
6) 1A and 7A groups in the periodic table: This AR application allows the user to observe the structure and the symbols of the 1A and 7A elements while manipulating the cards to explore the electronic structure of atoms of elements 1A and 7A.
7) Polarity of water: this application was made to introduce the concept of polarity between different compounds (such as H2O and CH4).
Conclusion
Augmented reality is a relatively new technology, mostly used in commercial and gaming but barely in chemical structure learning. AR can provide a great opportunity to learn complex structures in 3D format. Fortunately, some applications are currently available to be performed on smartphones to ease learning and investigating chemistry
Applying augmented reality in chemical structures will be a paramount important part of the future education system. If you want highly professional chemical structures or graphical abstracts, you can order your request or contact with the Inmywork.com team.