Nowadays, not only we see strong cooperation between different sciences, but also close correlation can be found between the sciences and art. As the results of this correlation, different products have been created ingeniously that could make big changes in the world of technology. The cooperation of chemistry as a science and art in the use of thermochromic pigments is one of the most famous examples since the invention has incredibly affected different industries.
What are the thermochromic pigments?
An excellent thermochromic pigments that exhibit a reversible and sharp metachromatism (a conspicuous, reversible change from a color to a colorless transparency or from one color to another one, and the background can be optionally revealed or hidden in a reversible reaction) at temperatures in a range of from -40° to 80° C can be organized of (a) a compound containing a phenolic hydroxyl group; (b) an electron-donating, chromatic organic compound; (c) a compound selected from the group consisting of higher aliphatic monovalent acid alcohol esters; and (d) a compound selected from the group consisting of higher aliphatic monovalent alcohols. Component (c) affects the sharpness and the temperature of coloration/decoloration and component (d) affects the temperature of coloration/decoloration.
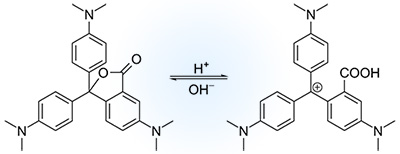
For instance, a mixture of different chemicals such as benzotriazole (a weak acid), crystal violet lactone (the color-changing dye itself), and a quaternary ammonium salt of a fatty acid (myristylammonium oleate) dissolved in 1-dodecanol as the solvent can be used as a kind of thermochromic pigments. These chemicals create a reversible chemical reaction in answer to changes in temperature that produces a change of color in products.
How do thermochromic pigments work?
To illustrate the mechanism of the thermochromic pigments please pay attention to the mixture shown above. This mixture is solid at low temperatures. A colored complex is formed by the reaction between the weak acid and the dye by causing the lactone ring in the center of the dye molecule to open. At high temperatures, more than 24–27 °C, the solvent starts to melt and the ammonium salt dissociates. This condition allows the ammonium salt to react with the weak acid. As a result of this reaction, the pH is increased, which leads the closing of the lactone ring of the dye to refer it to its colorless form.
Consequently, at high temperatures the capsules become colorless and the color of the fabric prevails, while at the low temperature the color is the combination of the color of the dyed fabric with the encapsulated colored dye.
Optimization and different utilities of thermochromic pigments in the industry
The excellent thermochromic characteristics of such a thermochromic pigment can be further improved when it is occluded in fine microcapsules having a size not exceeding 50 μm. Additionally, it is found that if the mentioned metachromatic system is combined with another material, it can be an excellent thermochromic material.
Thermochromic printing inks, thermochromic writing instruments, thermochromic polymers, thermochromic paints, thermochromic sheets and thermochromic cloth are the most famous usages of thermochromic pigments in products especially when they are optimized and are made of microencapsulated thermochromic materials having excellent thermochromatic characteristics.

Journal of Chemical Education Vol. 76 No. 6 June 1999 ,737
The correlation between art and science
As explained in this article, we observed an interesting example of the cooperation of art and science. The scientists in this field combine the world of colors, designs and chemistry to create new and special products. This kind of cooperation can be used to create creative products as you see below.

Crown’s Reveal temperature sensitive inks
If you are working on scientific projects related to electrochromic and thermochromic materials, you can ask the inmywork team for graphical design of their process or mechanism.




Leave A Comment